1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
| #ifndef TIME_WHEEL_TIMER
#define TIME_WHEEL_TIMER
#include <time.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 64
class tw_timer;
struct client_data {
sockaddr_in address;
int sockfd;
char buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
tw_timer* timer;
};
class tw_timer {
public:
tw_timer(int rot, int ts) : next(NULL), prev(NULL), rotation(rot), time_slot(ts) {}
int rotation;
int time_slot;
void (*cb_func)(client_data*);
client_data* user_data;
tw_timer* next;
tw_timer* prev;
};
class time_wheel {
public:
time_wheel() : cur_slot(0) {
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
slots[i] = NULL;
}
}
~time_wheel() {
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
while(tmp) {
slots[i] = tmp->next;
delete tmp;
tmp = slots[i];
}
}
}
tw_timer* add_timer(int timeout) {
if (timeout < 0) {
return NULL;
}
int ticks = 0;
if (timeout < SI) {
ticks = 1;
} else {
ticks = timeout / SI;
}
int rotation = ticks / N;
int ts = (cur_slot + (ticks % N)) % N;
tw_timer* timer = new tw_timer(rotation, ts);
if (!slots[ts]) {
printf("add timer, rotation is %d, ts is %d, cur_slot is %d\n", rotation, ts, cur_slot);
slots[ts] = timer;
} else {
timer->next = slots[ts];
slots[ts]->prev = timer;
slots[ts] = timer;
}
return timer;
}
void del_timer(tw_timer* timer) {
if (!timer) {
return;
}
int ts = timer->time_slot;
if (timer == slots[ts]) {
slots[ts] = slots[ts]->next;
if (slots[ts]) {
slots[ts]->prev = NULL;
}
delete timer;
} else {
timer->prev->next = timer->next;
if (timer->next) {
timer->next->prev = timer->prev;
}
delete timer;
}
}
void tick() {
tw_timer* tmp = slots[cur_slot];
printf("current slot is %d\n", cur_slot);
while (tmp) {
printf("tick the timer once\n");
if (tmp->rotation > 0) {
tmp->rotation--;
tmp = tmp->next;
} else {
tmp->cb_func(tmp->user_data);
if (tmp == slots[cur_slot]) {
printf("delete header in cur_slot\n");
slots[cur_slot] = tmp->next;
delete tmp;
if (slots[cur_slot]) {
slots[cur_slot]->prev = NULL;
}
tmp = slots[cur_slot];
} else {
tmp->prev->next = tmp->next;
if (tmp->next) {
tmp->next->prev = tmp->prev;
}
tw_timer* tmp2 = tmp->next;
delete tmp;
tmp = tmp2;
}
}
}
cur_slot = ++cur_slot % N;
}
private:
static const int N = 60;
static const int SI = 1;
tw_timer* slots[N];
int cur_slot;
}
#endif
|
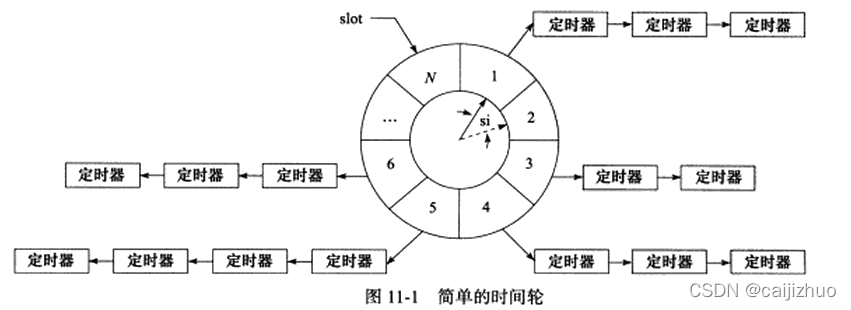
结构如图所示: 
图片来自高性能服务器编程——游双
$time\ slot = (current\ slot + (time\ interval / slot\ interval)) \ %\ N$
其中,$time\ slot$为需要添加到的时间槽,$current\ slot$为现在时间轮所处的时间槽,$time\ interval$为从现在开始计时,需要多久触发执行任务的时间,$slot\ interval$为每个时间槽所代表的时间。$N$为时间槽总数。
想要提高定时精度,使$slot\ interval$值变小。提高执行效率,增大$N$。
添加定时器时间复杂度$O(1)$,执行定时器时间复杂度$O(N)$,实际上效率比$O(N)$快,因为不同定时器被散列到不同的链表上了。当用多个时间轮时,该时间复杂度近似为$O(1)$。
reference:高性能linux服务器编程——游双